شفوية السياط المنيلية
| Chilomastix mesnili | |
|---|---|
| |
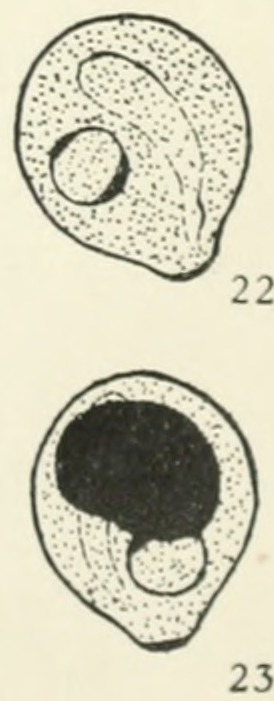
| Cysts of Chilomastix mesnili Fig. 22: The cytostome and nucleus clearly visible. Size 8.5 μm × 7.5 μm Fig. 23: The cytostome and nucleus partially obscured by large deeply staining mass of glycogen. Size 8.5 μm×7.5 μm | |
| التصنيف العلمي | |
| Domain: | |
| (unranked): | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | C. mesnili
|
| Binomial name | |
| Chilomastix mesnili (Wenyon, 1910)
| |
شفوية السياط المنيلية Chilomastix mesnili
غالباً غير مرضية إلا إذا كانت بأعداد كبيرة أو تشاركت مع الجيارديا وهي أصغر من الحيارديا، شكلها يشبه الجزيرة لها 3 سياط من الأعلى للحركة الأمامية و السوط الرابع داخل الثغير (فم صغير )، و تحوي ميزابة تلتف حول الالخلية بشكل حلزوني لتعطيها حركة حلزونية أمامية . الأبعاد (15 ميكرون )تتكيس أكياس صغيرة بيضوية تحوي نواة واحدة ،أفضل تلوين لها باليود اليودي لأن غشاءهاالخارجي يتلون .
Chilomastix mesnili is a parasite.[1] It infects about 3.5% of the population in the الولايات المتحدة. It is found in humans, chimpanzees, orangutans, monkeys, and pigs. It lives in the cecum and colon. C. mesnili has a similar life style to Giardia lamblia.
Although Chilomastix mesnili is considered non-pathogenic, it often occurs with other parasite infections. C. mesnili may be confused with other pathogenic species during diagnosis. It can create a false positive which would result in unnecessary treatment or a false negative which would withhold necessary treatment.
انظر ايضا
الهامش
- ^ B. Levecke, P. Dorny, T. Geurden, F. Vercammen & J. Vercruysse (2007). "Gastrointestinal protozoa in non-human primates of four zoological gardens in Belgium". Veterinary Parasitology. 148 (3–4): 236–246. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2007.06.020. PMID 17656023.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
المصادر
Schmidt, G. and Roberts, L. 2005. Foundations of Parasitology (7th ed.), New York: McGraw-Hill