حوض إولميدان
| Iullemmeden Basin | |
|---|---|
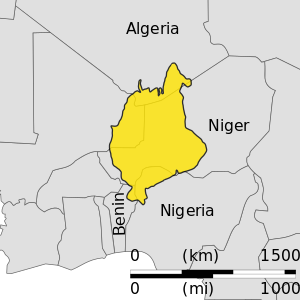 Location of the Iullemmeden Basin | |
| الإحداثيات | 17°54′N 5°36′E / 17.9°N 5.6°E |
| أصل التسمية | Iullemmeden |
| الموقع | Africa |
| المنطقة | Azawagh |
| البلد | |
| Characteristics | |
| بري/بحري | Onshore |
| الحدود | Aïr Mountains (NE) |
| المساحة | 1،000 km × 800 km (620 mi × 500 mi) |
| الهيدرولوجيا | |
| الأنهار | Niger River |
| Geology | |
| نوع الحوض | Intercratonic basin |
| الصفيحة | African |
| التجبل | Pan-African |
| العمر | Permo-Triassic-Pleistocene |
| علم طبقات الأرض | Stratigraphy |
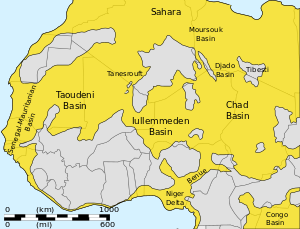
The Iullemmeden Basin (Berber language: Iwellemmedden) is a major sub-Saharan inland basin in West Africa, extending about 1،000 كيلومتر (620 mi) north to south and 800 كيلومتر (500 mi) east to west. It covers western Niger and parts of Algeria, Mali and Nigeria. It is named after the Iullemmeden, a federation of Tuareg people who live in the central region of Niger.[1] Its geographic range is largely coincident with the Azawagh region.[2]
Description
The area of the Iullemmeden Basin seems to have started to subside in Permo-Triassic times, and to have experienced gradual downwarping during the Late Cretaceous to Paleogene times, while steadily filling with sediment. Two prominent fault trends run NNE-SSW through the center of the basin, while WSW-ENE faults trends are found in the northeast of the basin near the Aïr Mountains.[1]
Stratigraphy
The sediments from Cambrian to Pleistocene times are 1،500 إلى 2،000 متر (4،900 إلى 6،600 ft) thick, with alternating layers formed when the basin was undersea and above sea level. Potentially valuable minerals include uranium and copper ores and coal and salt deposits. Niger is one of the world's largest producers of uranium.[3]
Formations of the Iullemmeden Basin
- Gwandu Formation
- Kalambaina Formation
- Wurno Formation
- Taloka Formation
- Dukamaje Formation
- Igdaman Group
- Majias Group
- Zoo Baba Formation
- Alanlara Formation
- Tegama Group
- Ilrhazer Group
- Téfidet Group
- Agadez Group[4]
- Izégouandane Group[4]
See also
References
- ^ أ ب Richard C. Selley (1997). "The Iullemmeden Basin". African basins. Elsevier. p. 89ff. ISBN 0-444-82571-1.
- ^ Paris, 1995
- ^ "URANIUM GEOLOGY: NIGER, WEST AFRICA" (PDF). NWT Uranium Corporation. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-14. Retrieved 2010-12-18.
- ^ أ ب Young et al., 2017, p.379
Bibliography
- Paris, François (1995). "L Bassin de I'Azawagh : peuplements et civilisations, du néolithique à l'arrivée de l'islam" (PDF). Milieux, sociétés et archéologues (in الفرنسية). Karthala. p. 228. Retrieved 3 April 2012.
- Young, Mark T.; Hastings, Alexander K.; Allain, Ronan; Smith, Thomas J. (2017), "Revision of the enigmatic crocodyliform Elosuchus felixi de Lapparent de Broin, 2002 from the Lower–Upper Cretaceous boundary of Niger: potential evidence for an early origin of the clade Dyrosauridae", Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society 179: 377–403
Further reading
- "ICONS atlas: AFR - Iullemmeden Basin". Earth Byte. Retrieved 2010-12-18.
- Pages using gadget WikiMiniAtlas
- Coordinates not on Wikidata
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- Pages with empty portal template
- CS1 الفرنسية-language sources (fr)
- Sedimentary basins of Africa
- Landforms of Algeria
- Landforms of Mali
- Landforms of Niger
- Landforms of Nigeria
- Landforms of Benin
- Geology of Algeria
- Geology of Mali
- Geology of Niger
- Geology of Nigeria
- Geology of Benin