اللغات الهندية الآرية
(تم التحويل من Indo-Aryan language)
| Indo-Aryan | |
|---|---|
| Indic | |
| Geographic distribution | — |
| Linguistic classification | الهندو-اوروپية
|
| Subdivisions |
|
| ISO 639-2 / 5 | inc |
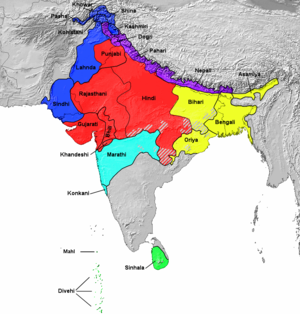 Geographical distribution of the major Indo-Aryan languages (Urdu is not shown because it is mainly a lingua franca with no prevalence as a first language. Outside of the scope of the map is the migratory Romani language). | |
تصنيف
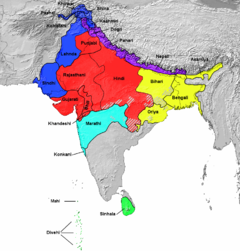
Indo-Aryan languages, grouping according to SIL Ethnologue:
Central zone
Northern zone
Northwestern zone
Eastern zone
Southern zone
Insular (Southern)
اللغات الهندو- أوربية
- الهندو- أوربية الكوردية القديمة
- الهندو - آرية الكوردية الحديثة
- الآريــة القديمة اللهجات الكوردية
اللغات القبتاريخية
- الهندو- اُربية البدائية
- التوجارية الانضولية البلطيقية السلافية الجرمانية
- الفريجية الارمينية السلتية الإيطالية
- السلينية التريشن اليديا البانيــة
- الهندو- آريـة
الهندو-آرية
- القزوينية الآرية القديمة الهندية الدردية
- التاتية
- التاليشية المازندرانية السنسكريتية
- الكيلانية
- الآرية القديمة
- البشتونية البلوجية السنديانية الفارسية القديمة
الفارسية الوسطى
- الكوردية القديمة
- الفارسية الحديثة
- الكوردية القديمة
اللهجات الزاكروسية
البهلوية الكوردية الوسطى الآفيستائية
- الكوردية الحديثة
- الكوردية الحديثة
- الكورمانجية الشمالية الكورمانجية الشرقية الكورمانجية الجنوبية
- الكورمانجية المنعزلة الكورمانجية الوسطى
- الكورمانجية الشمالية البهدنانية اللهجات
- الكورمانجية الشرقية الهورامية اللهجات
- الكورمانجية الجنوبية الفيلية اللهجات
- الكورمانجية المنعزلة اللهجات
- الكورمانجية الوسطى السورانية اللهجات
- الكورمانجية الشمالية
اللهجات البهدنانية
- البايزيدية الهكارية البوتانية
- الشمدينانية البهدنانية المركزية اللهجة الغربية
- الكورمانجية الشرقية
- اللهجات الهورامية
- الهورامية الغربية الهورامية الشرقية
- الكورمانجية الجنوبية
- اللهجات الفيلية
- الشبكية البختيارية اللورية المركزية الفيلية المركزية
الباجلانية الكوردلية اللكية الكلهورية
الشوهانية البايراوية الكورانية الاصلية الملكشاهية
الاركوازية المامسانية الكوهكلوية الهماوندية
الكرمنشاهية الايلامية الخانقينية المندلاوية الكورمانجية المنعزلة الزازائية الشكاكية
الكورمانجية الوسطى
- اللهجات السورانية
- الموكريانية السورانية المركزية الاردلانية
- السليمانية الكرميانية
علم الأصوات الكلامية
الحروف الساكنة
Stop positions[1]
| [], [], [], [], [] | Hindi, Punjabi, Dogri, Sindhi, Gujarati, Bihari,Maithili, Sinhalese, Oriya, Standard Bengali, dialects of Rajasthani (except Lamani, NW. Marwari, S. Mewari) |
| [], [], [], [], [] | Nepali, E. and N. dialects of Bengali (Dacca, Maimansing, Rajshahi), dialects of Rajasthani (Lamani and NW. Marwari), Northern Lahnda's Kagani, Kumauni, many West Pahari dialects (not Chamba Mandeali, Jaunsari, or Sirmauri) |
| [], [], [], [], [], [] | Marathi, Konkani, certain W. Pahari dialects (Bhadrawahi, Bhalesi, Padari, Simla, Satlej, maybe Kulu), Kashmiri |
| [], [], [], [], [], [], [] | Shina, Bashkarik, Gawarbati, Phalura, Kalasha, Khowar, Shumashti, Kanyawali, Pashai |
| [], [], [], [] | Rajasthani's S. Mewari |
| [], [], [] | Assamese |
| [], [], [], [] | Romani |
| [], [] | Chittagonian |
الرسوم البيانية
The following are consonant systems of major and representative New Indo-Aryan languages, as presented in Masica (1991:106–107), though here they are in IPA. Parentheses indicate those consonants found only in loanwords: square brackets indicate those with "very low functional load". The arrangement is roughly geographical.
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
انظر أيضاً
- List of Indo-Aryan languages
- Indo-Aryans
- Indo-Iranians
- Indo-Aryan migration
- Proto-Vedic Continuity
- The family of Brahmic scripts
- Linguistic history of India
- Indo-Aryan loanwords in Tamil
المصادر
- ^ Masica (1991:94–95)
- John Beames, A comparative grammar of the modern Aryan languages of India: to wit, Hindi, Panjabi, Sindhi, Gujarati, Marathi, Oriya, and Bangali. Londinii: Trübner, 1872-1879. 3 vols.
- Cardona, George; Jain, Dhanesh, eds. (2003), The Indo-Aryan Languages, Routledge, ISBN 978-0-415-77294-5, http://books.google.com/books?id=jPR2OlbTbdkC&printsec=frontcover&dq=indo-aryan+languages.
- Madhav Deshpande (1979). Sociolinguistic attitudes in India: An historical reconstruction. Ann Arbor: Karoma Publishers. ISBN 0-89720-007-1, ISBN 0-89720-008-X (pbk).
- Chakrabarti,Byomkes (1994). A comparative study of Santali and Bengali. Calcutta: K.P. Bagchi & Co. ISBN 81-7074-128-9
- Erdosy, George. (1995). The Indo-Aryans of ancient South Asia: Language, material culture and ethnicity. Berlin: Walter de Gruyter. ISBN 3-11-014447-6.
- Kobayashi, Masato.; & George Cardona (2004). Historical phonology of old Indo-Aryan consonants. Tokyo: Research Institute for Languages and Cultures of Asia and Africa, Tokyo University of Foreign Studies. ISBN 4-87297-894-3.
- Masica, Colin (1991), The Indo-Aryan Languages, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-29944-2, http://books.google.com/books?id=J3RSHWePhXwC&printsec=frontcover&dq=indo-aryan+languages.
- Misra, Satya Swarup. (1980). Fresh light on Indo-European classification and chronology. Varanasi: Ashutosh Prakashan Sansthan.
- Misra, Satya Swarup. (1991–1993). The Old-Indo-Aryan, a historical & comparative grammar (Vols. 1-2). Varanasi: Ashutosh Prakashan Sansthan.
- Sen, Sukumar. (1995). Syntactic studies of Indo-Aryan languages. Tokyo: Institute for the Study of Languages and Foreign Cultures of Asia and Africa, Tokyo University of Foreign Studies.
- Vacek, Jaroslav. (1976). The sibilants in Old Indo-Aryan: A contribution to the history of a linguistic area. Prague: Charles University.
وصلات خارجية
- The Indo Aryan languages, 10-25-2009
- Transliteration of Indic Languages & Scripts (Anthony Stone)
- Survey of the syntax of the modern Indo-Aryan languages (Rajesh Bhatt), February 7, 2003.
This article contains content from Wikimedia licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0. Please comply with the license terms.